Exponential Golomb coding
摘錄自維基百科,Exponential-Golomb coding (或稱 Exp-Golomb code) 是一種 Universal code,也就是 Exp-Golomb code 能夠映射到所有正整數。
假設輸入為 x ,其編碼步驟為:
- 以二進位寫下
x + 1 - 數
x + 1的二進位數字總共有多少位數,並在x + 1前面補上等同其位數減 1 的數量的0
Example 1:
x = 5
1. Write down 5 + 1 = 6 as binary "110".
2. "110" has 3 digits, we write 2 "0"s preceding "110".
The Exp-Golomb code of 5 is "00110".
Example 2:
x = 24
1. Write down 24 + 1 = 25 as binary "11001".
2. "11001" has 5 digits, we write 4 "0"s preceding "11001".
The Exp-Golomb code of 24 is "000011001".
按照上述規則計算 0 ~ 8 的 Exp-Golomb code:
x step 1 step 2
0 ⇒ 1 ⇒ 1
1 ⇒ 10 ⇒ 010
2 ⇒ 11 ⇒ 011
3 ⇒ 100 ⇒ 00100
4 ⇒ 101 ⇒ 00101
5 ⇒ 110 ⇒ 00110
6 ⇒ 111 ⇒ 00111
7 ⇒ 1000 ⇒ 0001000
8 ⇒ 1001 ⇒ 0001001
如果要讓 Exp-Golomb code 編碼有號整數,只需要讓有號數一一對應無號數即能達到目的:
x map step 1 step 2
0 ⇒ 0 ⇒ 1 ⇒ 1
1 ⇒ 1 ⇒ 10 ⇒ 010
−1 ⇒ 2 ⇒ 11 ⇒ 011
2 ⇒ 3 ⇒ 100 ⇒ 00100
−2 ⇒ 4 ⇒ 101 ⇒ 00101
3 ⇒ 5 ⇒ 110 ⇒ 00110
−3 ⇒ 6 ⇒ 111 ⇒ 00111
4 ⇒ 7 ⇒ 1000 ⇒ 0001000
−4 ⇒ 8 ⇒ 1001 ⇒ 0001001
我們可以按照順序,每 $2^i$ 個 Exp-Golomb code 分為一組。對於每個編碼,前面有 $i$ 個 0 就代表該編碼屬於 $S_i$ ,每個編碼正中央紅色的 1 作為分界點,後綴的編碼以二進位表示為第 $S_i$ 組的第 $j$ 個元素,記為 $G_{i,j}$ :
$ \ S_0 \quad \quad \quad S_1 \quad \quad \quad \quad \quad \quad \quad \quad \ \ S_2 \\ \{\color{red}1\},\ \{0\color{red}10,\ 0\color{red}11\},\ \{00\color{red}100,\ 00\color{red}101,\ 00\color{red}110,\ 00\color{red}111\},\ … \\ G_{0,0} \ \ \ G_{1,0} \ \ \ G_{1,1} \quad \quad G_{2,0} \quad \ \ G_{2,1} \quad \ \ G_{2,2} \quad \ G_{2,3}$
Order-k Exponential Golomb coding
接下來,對 Exp-Golomb code 的編碼方式一般化,前綴的 0 的數量一樣代表該編碼在第幾組,但是每一組的元素數量變為 $2^{i+k}$ 個,後綴的編碼也加長 $k$ 位,我們將這種編碼方式稱為 $k$ 階 Exp-Golomb code。以下為範例:
order-0
$ \ S_0 \quad \quad \quad S_1 \quad \quad \quad \quad \quad \quad \quad \quad \ \ S_2 \\ \{\color{red}1\},\ \{0\color{red}10,\ 0\color{red}11\},\ \{00\color{red}100,\ 00\color{red}101,\ 00\color{red}110,\ 00\color{red}111\},\ … \\ G_{0,0} \ \ \ G_{1,0} \ \ \ G_{1,1} \quad \quad G_{2,0} \quad \ \ G_{2,1} \quad \ \ G_{2,2} \quad \ G_{2,3}$
order-1
$ \ \quad S_0 \quad \quad \quad \quad \quad \quad \quad S_1 \quad \quad \quad \quad \quad \quad \quad \quad \quad \quad \quad S_2 \\ \{\color{red}10,\ \color{red}11\},\ \{0\color{red}100,\ 0\color{red}101,\ 0\color{red}110,\ 0\color{red}111\},\ \{00\color{red}1000,\ 00\color{red}1001,\ 00\color{red}1010,\ … \\ G_{0,0} \ \ G_{0,1} \quad \ G_{1,0} \quad G_{1,1} \quad G_{1,2} \quad G_{1,3} \quad \quad G_{3,0} \quad \quad \ G_{3,1} \quad \quad G_{3,2}$
order-2
$ \ \quad S_0 \quad \quad \quad \quad \quad \quad \quad \quad \quad \quad \quad \quad \quad \quad \quad \quad \quad \quad \quad \quad S_1 \\ \{\color{red}100,\ \color{red}101,\ \color{red}110,\ \color{red}111\},\ \{0\color{red}1000,\ 0\color{red}1001,\ 0\color{red}1010,\ 0\color{red}1011,\ 0\color{red}1100,\ 0\color{red}1101,\ 0\color{red}1110,\ 0\color{red}1111\},\ …\\ G_{0,0} \ \ \ G_{0,1} \ \ G_{0,2} \ \ G_{0,3} \quad \ \ \ G_{1,0} \quad \ \ G_{1,1} \quad \ \ G_{1,2} \quad \ \ G_{1,3} \quad \ \ G_{1, 4} \quad \ \ G_{1, 5} \quad \ \ G_{1, 6} \quad \ G_{1, 7}$
產生 $k$ 階 Exp-Golomb code 的步驟為:
- 以二進位寫下 $x+2^k$
- 數 $x+2^k$ 的二進位數字總共有多少位數,並在
x + 1前面補上等同其位數減 $k$ 的數量的0
| x | order-0 | order-1 | order-2 | order-3 | order-4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 1 | 10 | 100 | 1000 | 10000 |
| 1 | 010 | 11 | 101 | 1001 | 10001 |
| 2 | 011 | 0100 | 110 | 1010 | 10010 |
| 3 | 00100 | 0101 | 111 | 1011 | 10011 |
| 4 | 00101 | 0110 | 01000 | 1100 | 10100 |
| 5 | 00110 | 0111 | 01001 | 1101 | 10101 |
| 6 | 00111 | 001000 | 01010 | 1110 | 10110 |
| 7 | 0001000 | 001001 | 01011 | 1111 | 10111 |
| 8 | 0001001 | 001010 | 01100 | 010000 | 11000 |
| 9 | 0001010 | 001011 | 01101 | 010001 | 11001 |
| 10 | 0001011 | 001100 | 01110 | 010010 | 11010 |
| 11 | 0001100 | 001101 | 01111 | 010011 | 11011 |
| 12 | 0001101 | 001110 | 0010000 | 010100 | 11100 |
C 語言實作
github repo: https://github.com/blueskyson/Exponential-Golomb-coding
如何使用
首先將 repo 中的 exp-golomb.c 編譯成 encode ,再將 decode 連結至 encode 即完成編譯:
$ gcc exp-golomb.c -o encode
$ ln -s encode decode
encode 和 decode 的參數格式如下,以下將 sample_text.txt 轉成 order-4 exp-golomb code 的方法:
# Usage
encode [input file] [output file] [order-k]
decode [input file] [output file] [order-k]
# Example
./encode sample_text.txt text.encode 4
./decode text.encode text.decode 4
主程式
這個小程式能將資料以 uint8_t 為一個單位編碼成 exp-golomb code ,在程式第 7 行,先設定 MAX_ORDER ,也就是程式能容許的 order-k 的限度,此程式最大的限度為 order-31 ,因為在轉換的過程是以 1 到 2 個 uint32_t 作為中繼的容器,如果 MAX_ORDER 大於等於 32 會造成編碼後的資料跨越 3 個 uint32_t ,我的沒有設計相應機制處理。
接下來設定 BUFFER_SIZE ,這個 macro 決定暫存陣列的長度。在 encode 函式中,暫存陣列為 uint32_t buffer[BUFFER_SIZE] ;在 decode 函式中,暫存陣列為 uint8_t buffer[BUFFER_SIZE]。
當 buffer 的元素達到 WRITE_SIZE 時便會將 buffer 的內容寫入 output file 並的清空 buffer 。
接下來我將 input file 以 file descriptor 的形式開啟,之後使用 mmap 讀檔、 output file 以 FILE* 的形式開啟,以 fwrite 寫入。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdint.h>
#include <libgen.h> //basename
#include <fcntl.h> //open
#include <unistd.h> //close
#include <sys/mman.h> //mmap
#include <sys/stat.h>
#define MAX_ORDER 7 // must be smaller than 32
#define BUFFER_SIZE 100
#define WRITE_SIZE (BUFFER_SIZE - 2)
/* function status */
#define FAIL 0
#define SUCCESS 1
int encode(int, FILE*, int);
int decode(int, FILE*, int);
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
if (argc < 3) {
puts("Usage:\n"
"encode [input file] [output file] [order-k]\n"
"decode [input file] [output file] [order-k]");
return 0;
}
/* open argv[1] as input file */
int in_fd = open(argv[1], O_RDONLY);
if (in_fd < 0) {
puts("cannot open input file");
return 0;
}
/* open argv[2] as output file */
FILE *out_file = fopen(argv[2], "wb");
if (!out_file) {
puts("cannot open output file");
return 0;
}
/* use argv[3] as order */
long int order = 0;
if (argc >= 4) {
char* endptr;
order = strtol(argv[3], &endptr, 10);
if (endptr == argv[3]) {
puts("order is not a decimal number");
return 0;
}
if (order > MAX_ORDER) {
puts("order larger than max order");
return 0;
}
}
int status;
if (strcmp(basename(argv[0]), "encode") == 0) {
status = encode(in_fd, out_file, order);
} else {
status = decode(in_fd, out_file, order);
}
fclose(out_file);
close(in_fd);
if (status == FAIL) {
remove(argv[2]);
}
return 0;
}
Encode
以 uint8_t* 型態打開 input file 的 mmap ,轉換後的 exp-golomb code 會緊密排列在 uint32_t 的陣列中,如下圖示:
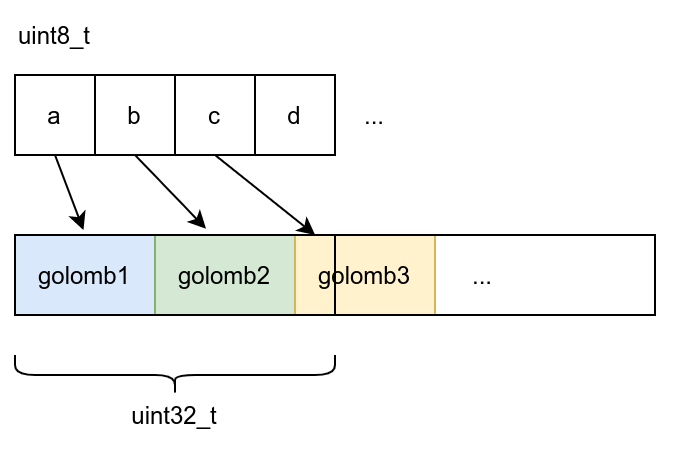
這裡所使用的編碼方法跟維基百科提到的一樣:
- 以二進位寫下 $x+2^k$
- 數 $x+2^k$ 的二進位數字總共有多少位數,並在 $x+2^k$ 前面補上等同其位數減 $(k+1)$ 的數量的
0
當轉換完所有資料後,在檔案尾加上一個 (uint32_t) 1 作為結束檔案的記號。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
int encode(int in_fd, FILE* out_file, int order)
{
struct stat s;
if (fstat(in_fd, &s) < 0) {
puts("cannot get status of iniput file");
return FAIL;
}
uint8_t *map = (uint8_t*) mmap(0, s.st_size, PROT_READ, MAP_PRIVATE, in_fd, 0);
if (map == MAP_FAILED) {
puts("cannot open mmap");
return FAIL;
}
uint32_t buffer[BUFFER_SIZE];
memset(buffer, 0, sizeof(buffer));
int buffer_index = 0;
int cursor = 32;
uint32_t offset = 1 << order;
/* start to encode */
for (long int i = 0; i < s.st_size; i++) {
uint32_t current = (uint32_t) map[i];
current += offset;
int clz = __builtin_clz(current);
int unary_width = 31 - clz - order;
int binary_width = 32 - clz;
/* write unary */
cursor -= unary_width;
if (cursor <= 0) {
cursor += 32;
buffer_index++;
}
/* write binary */
if (cursor < binary_width) { // truncate in uint32_t
buffer[buffer_index++] |= current >> (binary_width - cursor);
buffer[buffer_index] |= current << (32 - (binary_width - cursor));
cursor = cursor + 32 - binary_width;
} else {
buffer[buffer_index] |= current << (cursor - binary_width);
cursor -= binary_width;
}
/* write buffer */
if (buffer_index >= WRITE_SIZE) {
fwrite(buffer, 4, WRITE_SIZE, out_file);
uint32_t tail = buffer[buffer_index];
memset(buffer, 0, sizeof(buffer));
buffer[0] = tail;
buffer_index = 0;
}
}
/* finalize */
buffer[buffer_index + 1] = (uint32_t) 1; //end signal
fwrite(buffer, 4, buffer_index + 2, out_file);
return SUCCESS;
}
Decode
這裡只要將 encode 的步驟反著做就好了,以 uint32_t* 型態打開 input file 的 mmap ,轉換後的資料會轉型成 uint8_t 。唯一需要注意的是,讓 uint32_t 左移或右移 32 bit 時,會發生 [-Wshift-count-overflow] ,所以在以下程式碼的第 58 行寫了一個判斷去規避平移 32 bit 。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
int decode(int in_fd, FILE* out_file, int order)
{
struct stat s;
if (fstat(in_fd, &s) < 0) {
puts("cannot get status of iniput file");
return FAIL;
}
uint32_t *map = (uint32_t*) mmap(0, s.st_size, PROT_READ, MAP_PRIVATE, in_fd, 0);
if (map == MAP_FAILED) {
puts("cannot open mmap");
return FAIL;
}
uint8_t buffer[BUFFER_SIZE];
memset(buffer, 0, sizeof(buffer));
int buffer_index = 0;
int cursor = 32;
uint32_t offset = 1 << order;
int map_index = 0;
uint32_t current = map[0];
while (1) {
/* read unary */
int unary_width = 0;
if (current == 0) { // truncate in unary field
current = map[++map_index];
int clz = __builtin_clz(current);
unary_width = cursor + clz;
cursor = 32 - clz;
} else {
int clz = __builtin_clz(current);
unary_width = clz - (32 - cursor);
cursor = 32 - clz;
}
/* end of file is (uint32_t) 1 ,
* the leading zero of end of file is 31 */
if (unary_width >= 31) {
break;
}
/* read binary */
int binary_width = unary_width + 1 + order;
uint32_t tmp = 0;
if (binary_width > cursor) { // truncate in binary field
tmp = current << (binary_width - cursor);
current = map[++map_index];
binary_width -= cursor;
cursor = 32;
}
tmp |= current >> (cursor - binary_width);
tmp -= offset;
buffer[buffer_index++] = (uint8_t) tmp;
/* be careful for left shift 32 bits */
cursor -= binary_width;
if (cursor == 0) {
current = 0;
} else {
int shift = 32 - cursor;
current = (current << shift) >> shift;
}
if (buffer_index == BUFFER_SIZE) {
fwrite(buffer, 1, BUFFER_SIZE, out_file);
buffer_index = 0;
}
}
/* finalize */
if (buffer_index != 0) {
fwrite(buffer, 1, buffer_index, out_file);
}
return SUCCESS;
}
使用 perf 觀察效能
Encode
# perf stat --repeat 5 -e cache-misses,cache-references,instructions,cycles,context-switches,branches,branch-misses ./encode 74-0.txt 74-0.encode
Performance counter stats for './encode 74-0.txt 74-0.encode' (5 runs):
5,4589 cache-misses # 32.056 % of all cache refs ( +- 20.69% ) (45.64%)
17,0295 cache-references ( +- 4.66% ) (97.83%)
2515,6815 instructions # 1.46 insn per cycle ( +- 0.56% )
1718,9863 cycles ( +- 0.80% )
1 context-switches ( +- 40.82% )
267,6514 branches ( +- 3.97% ) (54.36%)
<not counted> branch-misses ( +-100.00% ) (2.17%)
0.006105 +- 0.000246 seconds time elapsed ( +- 4.02% )
Decode
# perf stat --repeat 5 -e cache-misses,cache-references,instructions,cycles,context-switches,branches,branch-misses ./decode 74-0.encode 74-0.decode
Performance counter stats for './decode 74-0.encode 74-0.decode' (5 runs):
7,6270 cache-misses # 32.452 % of all cache refs ( +- 20.52% ) (34.36%)
23,5021 cache-references ( +- 12.40% ) (77.71%)
2955,5866 instructions # 1.32 insn per cycle ( +- 2.98% ) (96.42%)
2245,0086 cycles ( +- 5.05% )
1 context-switches ( +- 25.00% )
298,9814 branches ( +- 2.96% ) (69.22%)
<not counted> branch-misses ( +- 28.11% ) (22.29%)
0.00845 +- 0.00136 seconds time elapsed ( +- 16.08% )
為了讓程式執行的夠久,讓 perf 能有效偵測效能,我使用 74-0.txt (湯姆歷險記) 進行測試,但是仍然無法測出 branch-misses 不知道是系統權限沒設定好或是要讓程式執行更久才能統計出來。
我對 order-0 的 encode 和 decode 測試 5 次,得到上面兩份數據,很明顯發現我的 cache-misses 非常高,平均高達 32% ,代表我程式寫法對變數的 locality 處理非常差,我認為這是目前值得我去改進的部份。我初步猜測可能原因是類似 copy 和 reference 機制的問題,也就是我常用的變數沒有配置在相鄰的 heap 中。
Exponential Golomb coding 效能分析
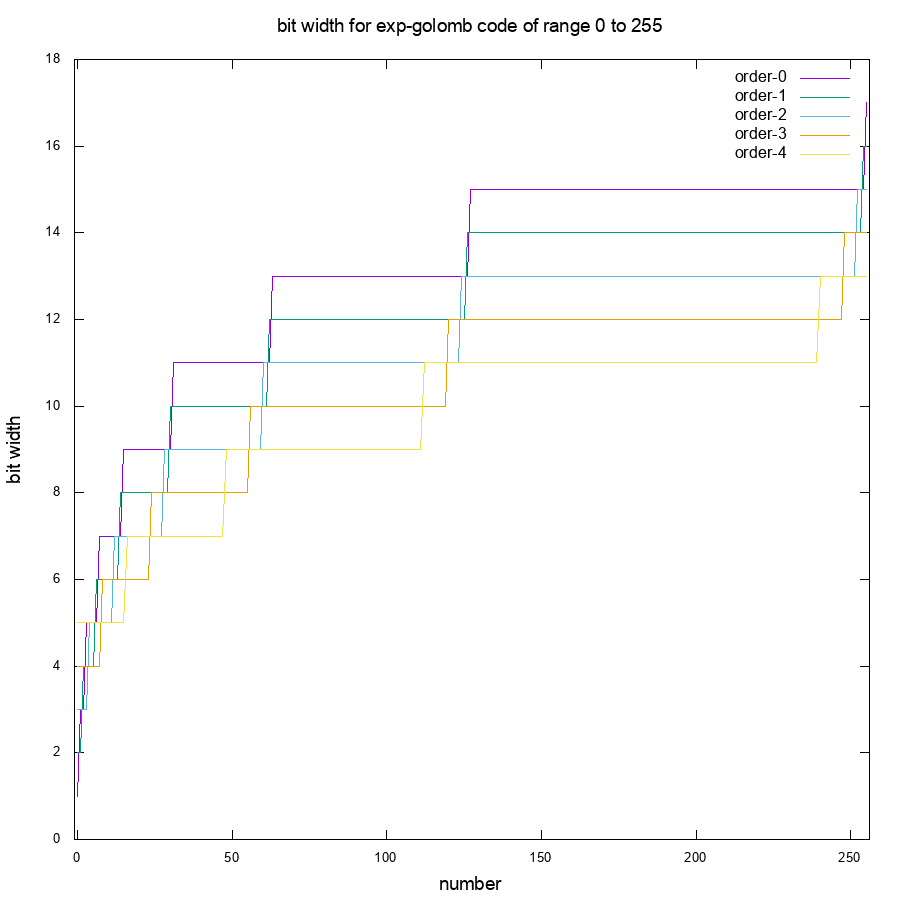
下圖是 8-bit 數值經過 order 0 到 4 的編碼後所佔據的位元長度,可以看到除了 order-4 之外,其他 exp-golomb code 都在原數值大於 50 之前達到 8 bit 的長度。 ASCII code 中常用的數字和英文字母介於 48 的 ‘0’ 到 122 的 ‘z’ 之間,幾乎都是會讓 exp-golomb code 超過 8 bit 的區間,若沒有修改 exp-golomb 的機制,根本無法壓縮。
x-compressor 以不斷更新模型,盡量讓出現頻率最高的數字使用位元長度較少的 golomb-rice code 達成壓縮的效果