Pointer Arithmetic
In the previous post, we mentioned that an array is actually a pointer. Array pointers support to return a shifted address via + operator and - operator. Now we learn how to shift an address of elements in array in pointer way.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
int main() {
int a[10], *p, *q;
for (int i = 0; i < 10; ++i) //init
a[i] = i * 10;
p = a; //assign an address
q = a + 5; //assign another address via pointer arithmetic
cout << "the address stored in p: " << p << endl;
cout << "the address stored in q: " << q << endl;
cout << "the value of p: " << *p << endl;
cout << "the value of q: " << *q << endl;
cout << endl;
cout << "the address in p + 2: " << p + 2 << endl;
cout << "the value of *(p + 2): " << *(p + 2) << endl;
cout << "the value of p[2]: " << p[2] << endl;
cout << "the address of q - 4: " << q - 4 << endl;
cout << "the value of *(q - 4): " << *(q - 4) << endl;
cout << "the value of q[3]: " << q[3] << endl;
return 0;
}
the address stored in p: 0x6dfebc
the address stored in q: 0x6dfed0
the value of p: 0
the value of q: 50
the address in p + 2: 0x6dfec4
the value of *(p + 2): 20
the value of p[2]: 20
the address of q - 4: 0x6dfec0
the value of *(q - 4): 10
the value of q[3]: 80
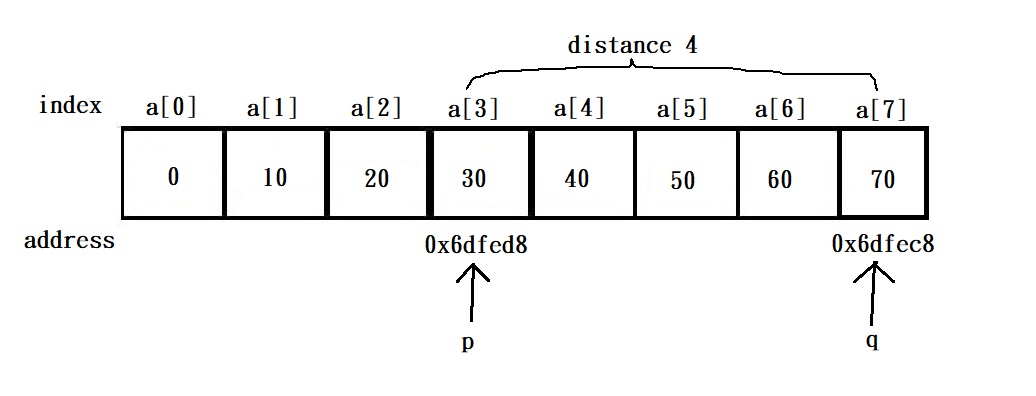
Besides shift pointer with an integer, we can subtract one pointers from another to get the distance of these two pointers.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
int main() {
int a[10], *p, *q;
for (int i = 0; i < 10; ++i) //init
a[i] = i * 10;
p = &a[7]; //assign an address
q = &a[3]; //assign another address via pointer arithmetic
cout << "the address stored in p: " << p << endl;
cout << "the address stored in q: " << q << endl;
cout << "the value of p: " << *p << endl;
cout << "the value of q: " << *q << endl;
cout << endl;
cout << "the distance from p to q: " << q - p << endl;
cout << "the distance from q to p: " << p - q << endl;
return 0;
}
the address stored in p: 0x6dfed8
the address stored in q: 0x6dfec8
the value of p: 70
the value of q: 30
the distance from p to q: -4
the distance from q to p: 4
Notice that subtracting two pointers pointing to different array will cause undefined behavior.
Combining the * and ++ Operators
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
int main() {
int a[10], *p;
for (int i = 0; i < 10; ++i) //init
a[i] = i * 10;
p = &a[7]; //assign an address
cout << "the address stored in p: " << p << endl;
cout << "the value of p: " << *p << endl;
cout << endl;
cout << "cout *p++ : " << *p++ << endl;
p = &a[7]; //keep p pointing to a[7]
cout << "cout *(p++) : " << *(p++) << endl;
p = &a[7];
cout << "cout (*p)++ : " << (*p)++ << endl;
a[7] = 70; //keep a[7] equaling 70
cout << "cout *++p : " << *++p << endl;
p = &a[7];
cout << "cout *(++p) : " << *(++p) << endl;
p = &a[7];
cout << "cout ++*p : " << ++*p << endl;
a[7] = 70;
cout << "cout ++(*p) : " << ++(*p) << endl;
a[7] = 70;
return 0;
}
the address stored in p: 0x6dfedc
the value of p: 70
cout *p++ : 70
cout *(p++) : 70
cout (*p)++ : 70
cout *++p : 80
cout *(++p) : 80
cout ++*p : 71
cout ++(*p) : 71
Using -- operator will demonstrate similar effects.
Pointer and Multidimensional Array
As we have said in Array and String, C++ stores arrays in row-major order. That means a multidimensional array is seen as a sequence of data assembled by many one dimensional arrays.
Use the features of pointer, we can process arrays easier. Here’s an example of initializing a three dimensional array:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
int arr[10][10][10];
//non-pointer process
for (int i = 0; i < 10; ++i)
for (int j = 0; j < 10; ++j)
for (int k = 0; k < 10; ++k)
arr[i][j][k] = 0;
//pointer process
int *p = &arr[0][0][0]; //the same as: int *p = arr;
for (; p <= &arr[9][9][9]; ++p)
*p = 0;
/*
By the way, Here is a faster initialization method.
This method can only be used to initialize elements to 0.
#include<cstring>
. . .
int arr[10][10][10]
memset(arr, '\0', sizeof(arr));
*/
We can also process single row of a multidimensional array
1
2
3
4
5
int arr[10][10][10];
int *p;
//initialize the 0th row of arr
for(p = arr[0][0]; p < arr[0][0] + 10; p++)
*p = 0;