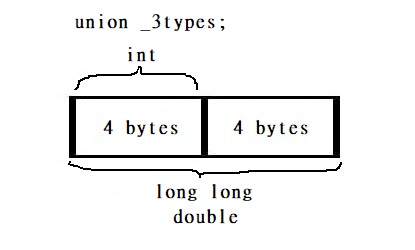
Union
A union, like a structure, consists of several members, possibly of different types. The compiler allocates only enough space for the largest of the members, which overlay each other within this space.
1
2
3
4
5
union _3types {
int int_val;
long long longlong_val;
double double_val;
};
We can access each type in different time.
1
2
3
4
5
_3types a;
a.int_val = 15; //store an int
cout << a.int_val;
a.double_val = 2.83; //store a double, int value is lost
cout << a.double_val;
When a structure member has more than one format, and these format won’t be used simultaneously, using union can save space.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
struct goods {
string name;
int amount;
int id_type;
union id_val { //two id formats
int num_id;
char[20] char_id;
} id;
};
...
//in main function
goods familymart[10];
for(int i=0; i<10; ++i) {
cin >> familymart[i].name;
cin >> familymart[i].amount;
cin >> familymart[i].id_type; //determine which type should be used to store id
if(familymart[i].id_type == 0) //if id_type is 0 then use int to store id
cin >> familymart[i].id.num_id;
else //else use char array to store id
cin >> familymart[i].id.char_id;
}
Enumeration
Besides the key word const, C++ provides enum for constant declaration. In many programs, we’ll need variables that have only a small set of meaningful values. For example, the suit of the rainbow spectrum should have 7 values: “red”, “orange”, “yellow”, “green”, “blue”, “indigo” and “violet”.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
enum spectrum {red, orange, yellow, green, blue, indigo, violet};
/*
this will construct red, orange, yellow ... int constants
their values are 0 ~ 6 in order
*/
...
spectrum color; //a variable of type spectrum
color = yellow; //valid, yellow is an enumerator
color++; //invalid, no operator ++, --, +=, -=
color = color + 1; //invalid, spectrum can't add int
color = red + orange; //invalid, the result of (red + orange) is converted to int
int color_int; //a variable of int
color_int = yellow; //valid, yellow is assigned to color_int as int
color_int = red + 3; //valid, red is converted to int while operating
color_int = red + yellow; //valid, both red and yellow are converted to int
We can also give each enumerator a specific value:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
enum bits {one = 1, two = 2, four = 4, eight = 8};
//specify every enumerator a value
enum pulse {first, second = 1000, third};
/*
in this example, the value of first is 0
the value of second is 1000
and third is grater then its previous enumerator by 1
so the value of third is 1001
*/
...
bits mybit;
mybit = bits(6); //valid, because 6 is in bits range
#define Preprocessor
Using macros to define a suit type and names:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
#define SPECTRUM int
#define RED 0
#define ORANGE 1
#define YELLOW 2
#define GREEN 3
#define BLUE 4
#define INDIGO 5
#define VIOLET 6
...
SPECTRUM color;
color = GREEN;
There are two main problems with this technique:
-
No indication that these macros represent values of the same set.
-
If there are too many possible values, defining separate macros will be tedious.